 |
Flecs v4.1
A fast entity component system (ECS) for C & C++
|
 |
Flecs v4.1
A fast entity component system (ECS) for C & C++
|
Queries enable games to quickly find entities that match a list of conditions, and are at the core of many Flecs features like systems, observers, tooling and serialization.
Flecs queries can do anything from returning entities that match a simple list of components, to matching complex patterns against entity graphs.
This manual contains a full overview of the query features available in Flecs. Some of the features of Flecs queries are:
and, or, not and optional operators.Transform component and a parent that have a Transform component.| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Id | An id that can be matched, added and removed |
| Component | Id with a single element (same as an entity id) |
| Pair | Id with two elements |
| Tag | Component or pair not associated with data |
| Relationship | Used to refer to first element of pair |
| Target | Used to refer to second element of pair |
| Source | Entity on which a term is matched |
| Iterator | Object used to iterate a query |
| Term | An element of a query that expresses a condition to match |
| Field | A single value or array of values made available by an iterator. An iterator usually provides a field per query term. |
Make sure to check out the query code examples in the repository:
Understanding the basic architecture of queries helps to make the right tradeoffs when using queries in games. The biggest impact on query performance is whether a query is cached or not. This section goes over what caching is, how it can be used and when it makes sense to use it.
Flecs is an archetype ECS, which means that entities with exactly the same components are grouped together in an "archetype" (also called a "table"). Archetypes are created on the fly whenever a new component combination is created in the ECS. For example:
Archetypes are important for queries. Since all entities in an archetype have the same components, and a query matches entities with specific components, a query can often match entire archetypes instead of individual entities. This is one of the main reasons why queries in an archetype ECS are fast.
The second reason that queries in an archetype ECS are fast is that they are cheap to cache. While an archetype is created for each unique component combination, games typically only use a finite set of component combinations which are created quickly after game assets are loaded.
This means that instead of searching for archetypes each time a query is evaluated, a query can instead cache the list of matching archetypes. This is a cheap cache to maintain: even though entities can move in and out of archetypes, the archetypes themselves are often stable.
If none of that made sense, the main thing to remember is that a cached query does not actually have to search for entities. Iterating a cached query just means iterating a list of prematched results, and this is really, really fast.
Flecs has both cached and uncached queries. If cached queries are so fast, why even bother with uncached queries? There are four main reasons:
As a rule of thumb, if you have a query that is evaluated each frame (as is typically the case with systems), they will benefit from being cached. If you need to create a query ad-hoc, an uncached query makes more sense.
Ad-hoc queries are often necessary when a game needs to find entities that match a condition that is only known at runtime, for example to find all child entities for a specific parent.
Queries can be created with a "cache kind", which specifies the caching behavior for a query. Flecs has four different caching kinds:
| Kind | C | C++ | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default | EcsQueryCacheDefault | flecs::QueryCacheDefault | Behavior determined by query creation context |
| Auto | EcsQueryCacheAuto | flecs::QueryCacheAuto | Cache query terms that are cacheable |
| All | EcsQueryCacheAll | flecs::QueryCacheAll | Require that all query terms are cached |
| None | EcsQueryCacheNone | flecs::QueryCacheNone | No caching |
The following sections describe each of the kinds.
When no cache kind is specified, queries will be created with the Default caching kind. A query with the Default kind will be created as cached (using the Auto kind, see next section) if a query is associated with an entity, and uncached if it isn't.
What does it mean for a query to be associated with an entity? When a query is created, an application can provide an entity to associate with the query. This binds the lifecycle of the query with that of the entity, and makes it possible to lookup the query (by name) in tools like the explorer.
The most common case of this is systems. Flecs systems have entity handles, which are associated with system queries. This means that all system queries by default are cached, unless specified otherwise.
The rationale behind this is that if a query is associated with an entity, it will likely be reused and outlive the scope in which the query is created. Queries that are reused many times across frames are good candidates for caching.
When the Auto kind is specified, all query terms that can be matched will be matched. Query features that rely on matching entire archetypes can typically be cached, whereas features that return individual entities cannot be cached. The following query features are cacheable:
$this source (default behavior, see variables)There are scenarios that are cacheable in theory but aren't cached yet by the current implementation. Over time the query engine will be extended to cache terms with variables, as long as they match entire archetypes.
Queries with the Auto kind can mix terms that are cached and uncached.
Queries with the All kind require all terms to be cacheable. This forces a query to only use features that can be cached. If a query with kind All uses features that cannot be cached, query creation will fail.
Queries with the None kind will not use any caching.
Queries that use traversal (either up or cascade) can trigger query "rematching". This is a process that ensures that a query cache that matches components on an entity reached through traversal stays up to date.
A typical example of this is a query that matched a Transform component on a parent entity. If the Transform component is removed from the parent it invalidates the cache, and rematching will happen.
Rematching can be an expensive process, especially in games with lots of archetypes. To learn if an application is slowed down by rematching, connect the explorer to it with the flecs::stats module imported (see the REST API manual), and inspect the world statistics page.
If rematching is taking up a significant amount of time, consider changing cached queries with traversal to uncached. This will increase query evaluation time, but should get rid of the query rematching cost.
Rematching is a temporary solution to a complex problem that will eventually be solved with a much cheaper mechanism. For now however, rematching is something that needs to be monitored for queries that use query traversal features.
Cached queries have an optimization where they store empty archetypes in a separate list from non-empty archetypes. This generally improves query iteration speed, as games can have large numbers of empty archetypes that could waste time when iterated by queries.
However, to keep empty archetypes and non-empty archetypes in separate lists, events have to be emitted from archetypes to queries whenever their state changes. When emitting these events becomes too expensive, games can opt out of empty archetype optimization, and instead periodically cleanup empty archetypes.
To do this, a query should be created with the EcsQueryMatchEmptyTables flag, and the ecs_delete_empty_tables function should be called periodically. An example:
C
C++
Rust
This will cause queries to return empty archetypes (iterators with count set to 0) which is something the application code will have to handle correctly.
This section explains how to create queries in the different language bindings and the flecs Flecs Query Language.
C
Query descriptors are the C API for creating queries. An example:
The example shows the short notation, which looks like this when expanded:
Note how component types are added with the ecs_id() macro. This translates the component type to the component id that queries require. Tags and pairs do not require the ecs_id() macro:
Query descriptors can also be used by the C++ API. However because C++ does not support taking the address of a temporary, and not all language revisions support designated initializers, query descriptors in C++ should be used like this:
Queries have to be deleted with the ecs_query_fini function, except when a query is associated with an entity. An example:
C++
Query builders are the C++ API for creating queries. The builder API is built on top of the descriptor API, and adds a layer of convenience and type safety that matches modern idiomatic C++. An example of a simple query:
Queries created with template arguments provide a type safe way to iterate components:
The builder API allows for incrementally constructing queries:
Rust
The query builder API is built on top of the term builder API, and adds a layer of convenience and type safety that matches modern idiomatic Rust. An example of a simple query:
Queries created with generic arguments provide a type safe way to iterate components:
The builder API allows for incrementally constructing queries, but also gives you access to more advanced features (see later sections):
Flecs Query Language
The Flecs Query Language is a string format that can be parsed into a query. The format is used by convenience macros in the C API like ECS_SYSTEM and ECS_OBSERVER, and makes it easier to create queries at runtime for tools like https://www.flecs.dev/explorer/. An example of a simple query in the DSL:
An example of how the DSL is used with the ECS_SYSTEM convenience macro:
Queries can be created from expressions with both the descriptor and builder APIs:
For more details on the syntax, see the Flecs Query Language manual.
This section describes the different ways queries can be iterated.
C
In the C API an iterator object of type ecs_iter_t can be created using the ecs_query_iter function. This iterator can then be iterated with ecs_query_next.
An iterator can also be iterated with the ecs_iter_next function which is slightly slower, but does not require knowledge about the source the iterator was created for.
An example:
Iteration is split up into two loops: the outer loop which iterates tables, and the inner loop which iterates the entities in that table. This approach provides direct access to component arrays, which allows compilers to do performance optimizations like auto-vectorization.
The indices provided to the ecs_field() function must correspond with the order in which terms have been specified in the query. This index starts counting from 0.
C++
C++ has two iteration functions, each and run. The each function is the default and often fastest approach for iterating a query in C++. An example:
A flecs::entity can be added as first argument:
A flecs::iter and size_t argument can be added as first arguments. This variant of each provides access to the flecs::iter object, which contains more information about the object being iterated. The size_t argument contains the index of the entity being iterated, which can be used to obtain entity-specific data from the flecs::iter object. An example:
When a query contains a template argument that is an empty type (a struct without any members), it should be passed by value instead of by reference:
Alternatively an empty type can be specified outside of the query type, which removes it from the signature of each:
The run function provides an initialized iterator to a callback, and leaves iteration up to the callback implementation. Similar to C query iteration, the run callback has an outer and an inner loop.
An example:
Entities can be moved between tables when components are added or removed. This can cause unwanted side effects while iterating a table, like iterating an entity twice, or missing an entity. To prevent this from happening, a table is locked by the C++ each and run functions, meaning no entities can be moved from or to it.
When an application attempts to add or remove components to an entity in a table being iterated over, this can throw a runtime assert. An example:
This can be addressed by deferring operations while the query is being iterated:
An application can also use the defer_begin and defer_end functions which achieve the same goal:
Code ran by a system is deferred by default.
Rust
Rust has two main iteration functions, each and run. The each function is the default and often fastest approach for iterating a query in Rust. Both each and run have some variances that offer slightly different functionality. These variances are each_entity, each_iter and run_each and run_iter.
An example:
A EntityView can be added as by using each_entity:
Using each_iter a TableIter and usize argument are added as first arguments. This variant of each provides access to the TableIter object, which contains more information about the object being iterated. The usize argument contains the index of the entity being iterated, which can be used to obtain entity-specific data from the TableIter object. An example:
A query can also contain generic arguments that is an empty type (a struct without any members).
Alternatively an empty type can be specified outside of the query type, which removes it from the signature of each:
The run function provides an initialized iterator to a callback, and leaves iteration up to the callback implementation. The run callback has an outer and an inner loop.
An example:
Entities can be moved between tables when components are added or removed. This can cause unwanted side effects while iterating a table, like iterating an entity twice, or missing an entity. To prevent this from happening, a table is locked in the Rust each and run functions, meaning no entities can be moved from or to it.
When an application attempts to add or remove components to an entity in a table being iterated over in not deferred context, this can throw a runtime assert. An example:
This can be addressed by deferring operations while the query is being iterated:
An application can also use the defer_begin and defer_end functions which achieve the same goal:
Code ran by a system is deferred by default.
This section goes over the different features of queries and how they can be expressed by the query descriptor API, query builder API and in the Flecs Query Language.
A component is any single id that can be added to an entity. This includes tags and regular entities, which are ids that are not associated with a datatype.
To match a query, an entity must have all the requested components. An example:
Only entities e2 and e3 match the query Position, Velocity.
The following sections describe how to create queries for components in the different language bindings.
C
To query for a component in C, the id field of a term can be set:
The id field is guaranteed to be the first member of a term, which allows the previous code to be rewritten in this shorter form:
The ecs_id macro converts the component typename into the variable name that holds the component identifier. This macro is required for components created with ECS_COMPONENT, but not when querying for regular tags/entities:
Components can also be queried for by name by setting the .first.name member in a term:
C++
An easy way to query for components in C++ is to pass them as template arguments to the query factory function:
This changes the returned query type, which determines the type of the function used to iterate the query:
The builder API makes it possible to add components to a query without modifying the query type:
When template arguments are mixed with the builder API, the components added by the term function will be placed after the components provided as template arguments.
The builder API makes it possible to query for regular entity ids created at runtime:
Components can also be queried for by name. To query for component types by name, they have to be used or registered first.
Rust
An easy way to query for components in Rust is to pass them as generic arguments to the query new function:
This changes the returned query type, which determines the type of the function used to iterate the query:
The builder API makes it possible to add components to a query without modifying the query type:
When generic arguments are mixed with the builder API, the components added by the term function will be placed after the components provided as generic arguments.
The builder API makes it possible to query for regular entity ids created at runtime:
Components can also be queried for by name. To query for component types by name, they have to be used or registered first.
Flecs Query Language
To query for a components in the Flecs Query Language they can be specified in a comma separated list of identifiers. The rules for resolving identifiers are the same as the ecs_lookup / world.lookup functions. An example:
Any named entity can be specified this way. Consider:
The entity e from this example will be matched by this query:
When an identifier in the Flecs Query Language consists purely out of numeric characters it is converted to an entity id. If in the previous example Npc has id 100 and Platoon_01 has id 101, the following query string would be equivalent:
The , symbol in the Flecs Query Language is referred to as the and operator, as an entity must have all comma-separated components in order to match the query.
Wildcards allow a single query term to match with more than one (component) ids. Flecs supports two kinds of wildcards:
| Name | DSL Symbol | C identifier | C++ identifier | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wildcard | * | EcsWildcard | flecs::Wildcard | Match all |
| Any | _ | EcsAny | flecs::Any | Match at most one |
The Wildcard wildcard returns an individual result for anything that it matches. The query in the following example will return twice for entity e, once for component Position and once for component Velocity:
C
C++
Rust
The Any wildcard returns a single result for the first component that it matches. The query in the following example will return once for entity e:
C
C++
Rust
When using the Any wildcard it is undefined which component will be matched, as this can be influenced by other parts of the query. It is guaranteed that iterating the same query twice on the same dataset will produce the same result.
Wildcards are particularly useful when used in combination with pairs (next section).
A pair is an id that encodes two elements. Pairs, like components, can be added to entities and are the foundation for Relationships.
The elements of a pair are allowed to be wildcards. When a query pair contains the Wildcard wildcard, a query returns a result for each matching pair on an entity. When a query pair returns an Any wildcard, the query returns at most a single matching pair on an entity.
The following sections describe how to create queries for pairs in the different language bindings.
C
To query for a pair in C, the id field of a term can be set to a pair using the ecs_pair macro:
The id field is guaranteed to be the first member of a term, which allows the previous code to be rewritten in this shorter form:
When an element of the pair is a component type, use the ecs_id macro to obtain the identifier to the id variable of the component type:
The ecs_isa, ecs_childof and ecs_dependson convenience macros can be used to create pairs for builtin relationships. The two queries in the next example are equivalent:
Pair queries can be created by setting their individual elements in the first.id and second.id members of a term:
Alternatively, one or both elements of a pair can be resolved by name. The two queries in the next example are equivalent:
When a query pair contains a wildcard, the ecs_field_id function can be used to determine the id of the pair element that matched the query:
C++
When both parts of a pair are types, a flecs::pair template can be used. Pair templates can be made part of the query type, which makes them part of the argument list of the iterator functions. An example:
Pairs can also be added to queries using the builder API. This allows for the pair to be composed out of both types and regular entities. The three queries in the following example are equivalent:
Individual elements of a pair can be specified with the first and second methods. The methods apply to the last added term. An example:
Individual elements of a pair can be resolved by name by using the first and second methods:
When a query pair contains a wildcard, the flecs::iter::pair method can be used to determine the id of the pair element that matched the query:
Rust
When both parts of a pair are types, a tuple can be used. tuple pairs can be made part of the query type, which makes them part of the argument list of the iterator functions. An example:
Tuple pairs can also be added to queries using the builder API. This allows for the pair to be composed out of both types and regular entities. The three queries in the following example are equivalent:
Individual elements of a tuple pair can be specified with the first and second methods. The methods apply to the last added term. An example:
Individual elements of a pair can be resolved by name by using the first and second methods:
When a query pair contains a wildcard, the TableIter::pair method can be used to determine the id of the pair element that matched the query:
Flecs Query Language
To query for a pair in the Flecs Query Language, the elements of a pair are a comma separated list surrounded by parentheses. An example:
A query may contain multiple pairs:
Queries for pairs that contain wildcards should use the symbols for either the Wildcard or Any wildcards:
A pair may contain two wildcards:
Access modifiers specify which components of a query can be read and/or written. The different access modifiers are:
| Name | DSL identifier | C identifier | C++ identifier | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In | in | EcsIn | flecs::In | Component is readonly |
| Out | out | EcsOut | flecs::Out | Component is write only |
| InOut | inout | EcsInOut | flecs::InOut | Component can be read/written |
| None | none | EcsInOutNone | flecs::InOutNone | Component is neither read nor written |
| Default | n/a | EcsInOutDefault | flecs::InOutDefault | Default modifier is selected for term |
Access modifiers can be used by API functions to ensure a component cannot be written, for example by requiring a component to be accessed with a const modifier. APIs may also infer access modifiers where possible, for example by using the In modifier for a query term with a type that has a const modifier.
When using pipelines, the scheduler may use access modifiers to determine where sync points are inserted. This typically happens when a system access modifier indicates a system writing to a component not matched by the query (for example, by using set), and is followed by a system that reads that component.
Access modifiers may also be used by serializers that serialize the output of an iterator (for example: ecs_iter_to_json). A serializer may for example decide to not serialize component values that have the Out or None modifiers.
When no access modifier is specified, Default is assumed. This selects InOut for components owned by the matched entity, and In for components that are from entities other than the one matched by the query.
When a query term can either match a component from the matched entity or another entity (for example: when a component is inherited from a prefab) the Default access modifier only provides write access for the results where the component is owned by the matched entity. This prevents accidentally writing to a shared component. This behavior can be overridden by explicitly specifying an access modifier.
When a query term matches a tag (a component not associated with data) with a Default modifier, the None modifier is selected.
The following sections show how to use access modifiers in the different language bindings.
C
Access modifiers can be set using the inout member:
C++
Access modifiers can be set using the inout method:
When the const modifier is added to a type, the flecs::In modifier is automatically set:
This also applies to types added with term:
When a component is added by the term method and retrieved from a flecs::iter object during iteration, it must meet the constraints of the access modifiers. If the constraints are not met, a runtime assert may be thrown:
The builder API has in(), inout(), out() and inout_none() convenience methods:
Rust
Access modifiers can be set using the set_inout_kind method:
When the const / immutable reference modifier is added to a type, the InOutKind::In modifier is automatically set:
This also applies to types added with term / with:
When a component is added by the term method or generic terms with the run method, you can retrieve it from a TableIter object during iteration with the field method.
The builder API has set_in(), set_inout(), set_out() and set_inout_none() convenience methods:
Flecs Query Language
Access modifiers in the Flecs Query Language can be specified inside of angular brackets before the component identifier:
The following operators are supported by queries:
| Name | DSL operator | C identifier | C++ identifier | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| And | , | EcsAnd | flecs::And | Match at least once with term |
| Or | \|\| | EcsOr | flecs::Or | Match at least once with one of the OR terms |
| Not | ! | EcsNot | flecs::Not | Must not match with term |
| Optional | ? | EcsOptional | flecs::Optional | May match with term |
| Equal | == | EcsPredEq | flecs::PredEq | Equals entity/entity name |
| Match | ~= | EcsPredMatch | flecs::PredMatch | Match entity name with substring |
| AndFrom | and \| | EcsAndFrom | flecs::AndFrom | Match all components from id at least once |
| OrFrom | or \| | EcsOrFrom | flecs::OrFrom | Match at least one component from id at least once |
| NotFrom | not \| | EcsNotFrom | flecs::NotFrom | Don't match any components from id |
The And operator is used when no other operators are specified. The following sections show how to use the And operator in the different language bindings.
C
When no operator is specified, And is assumed. The following two queries are equivalent:
C++
When no operator is specified, And is assumed. The following two queries are equivalent:
The builder API has a and_ convenience method:
Rust
When no operator is specified, And is assumed. The following two queries are equivalent:
The builder API has a and convenience method:
Flecs Query Language
Query expressions with comma separated lists use the And operator:
The Or operator allows for matching a single component from a list. Using the Or operator means that a single term can return results of multiple types. When the value of a component is used while iterating the results of an Or operator, an application has to make sure that it is working with the expected type.
When using the Or operator, the terms participating in the Or expression are made available as a single field. Field indices obtained from an iterator need to account for this. Consider the following query:
This query has 4 terms, while an iterator for the query returns results with 3 fields. This is important to consider when retrieving the field for a term, as its index has to be adjusted. In this example, Position has index 1, Velocity || Speed has index 2, and Mass has index 3.
The following sections show how to use the Or operator in the different language bindings.
C
To create a query with Or terms, set oper to EcsOr:
C++
To create a query with Or terms, use the oper method with flecs::Or:
The builder API has a or_ convenience method:
Rust
To create a query with Or terms, use the oper method with enum OperKind::Or:
The builder API has a or convenience method:
Flecs Query Language
To create a query with Or terms, use the || symbol:
The Not operator makes it possible to exclude entities with a specified component. Fields for terms that uses the Not operator will never provide data.
A note on performance: Not terms are efficient to evaluate when combined with other terms, but queries that only have Not terms (or `Optional`) can be expensive. This is because the storage only maintains indices for tables that have a component, not for tables that do not have a component.
The following sections show how to use the Not operator in the different language bindings.
C
To create a query with Not terms, set oper to EcsNot:
C++
To create a query with Not terms, use the oper method with flecs::Not:
The builder API has a not_ convenience method:
An application can also use the without method:
Rust
To create a query with Not terms, use the oper method with enum OperKind::Not:
The builder API has a not_ convenience method:
An application can also use the without method:
Flecs Query Language
To create a query with Not terms, use the ! symbol:
The Optional operator optionally matches with a component. While this operator does not affect the entities that are matched by a query, it can provide more efficient access to a component when compared to conditionally getting the component in user code. Before accessing the value provided by an optional term, code must first check if the term was set.
A note on performance: just like the Not operator Optional terms are efficient to evaluate when combined with other terms, but queries that only have Optional terms can be expensive. Because the Optional operator does not restrict query results, a query that only has Optional terms will match all entities.
When an optional operator is used in a query, and a variable written by the optional term is read by a subsequent term, the subsequent term becomes a dependent term. This means that if the optional term does not match, the dependent term will be ignored. For example:
Because the second term is optional, the variable $planet may or may not be set depending on whether the term was matched. As a result the third term becomes dependent: if $planet was not set, the term will be ignored.
The following sections show how to use the Optional operator in the different language bindings.
C
To create a query with Optional terms, set oper to EcsOptional:
C++
To create a query with Optional terms, a component can be specified as a pointer type:
Alternatively, an application can call the oper method with flecs::Optional:
The builder API has an optional convenience method:
Rust
To create a query with Optional terms, a component can be specified as an Option type:
Alternatively, an application can call the oper method with enum OperKind::Optional:
The builder API has an optional convenience method:
Flecs Query Language
To create a query with Optional terms, use the ? symbol:
Equality operators (==, !=, ~=) allow a query to ensure that a variable equals a specific entity, that the entity it stores has a specific name, or that the entity name partially matches a substring.
The left hand side of an equality operator must be a variable. The right hand side of an operator can be an entity identifier or a string for the == and != operators, and must be a string in case of the ~= operator. For example:
Test if variable $this equals Foo (Foo must exist at query creation time):
Test if variable $this equals entity with name Foo (Foo does not need to exist at query creation time):
Test if variable $this stores an entity with a name that has substring Fo:
When the equals operator (==) is used with a variable that has not yet been initialized, the right-hand side of the operator will be assigned to the variable. If the right hand side is a string, it will be used to lookup an entity by name. If the lookup fails, the term will not match.
Other than regular operators, equality operators are set as first, with the left hand being src and the right hand being second. Equality operators can be combined with And, Not and Or terms.
Terms with equality operators return no data.
C
C++
Rust
Flecs Query Language
The AndFrom, OrFrom and NotFrom operators make it possible to match a list of components that is defined outside of the query. Instead of matching the id provided in the term, the operators match the list of components of the provided id as if they were provided as a list of terms with And, Or or Not operators. For example, if entity e has components Position, Velocity and is combined in a query with the AndFrom operator, entities matching the query must have both Position and Velocity.
The AndFrom, OrFrom and NotFrom operators are especially useful when combined with prefab entities, which by default are not matched with queries themselves. Components that have the (OnInstantiate, DontInherit) property are ignored while matching the operators, which means that using a prefab in combination with AndFrom, OrFrom and NotFrom will not cause components like Prefab or ChildOf to be considered.
Component lists can be organized recursively by adding an id to an entity with the AND and OR id flags.
Fields for terms that use the AndFrom, OrFrom or NotFrom operators never provide data. Access modifiers for these operators default to InOutNone. When a AndFrom, OrFrom or NotFrom operator is combined with an access modifier other than InOutDefault or InOutNone query creation will fail.
The following sections show how to use the operators in the different language bindings.
C
To use the AndFrom, OrFrom and NotFrom operators, set oper to EcsAndFrom, EcsOrFrom or EcsNotFrom
C++
To use the AndFrom, OrFrom and NotFrom operators, call the oper method with flecs::AndFrom, flecs::OrFrom or flecs::NotFrom.
The builder API has the and_from, or_from and not_from convenience methods:
Rust
To use the AndFrom, OrFrom and NotFrom operators, call the oper method with enum OperKind::AndFrom, OperKind::OrFrom or flecs::NotFrom.
The builder API has the and_from, or_from and not_from convenience methods:
Flecs Query Language
To create a query with the AndFrom, OrFrom and NotFrom operators in the C API, use and, or and not in combination with the bitwise OR operator (|):
Query scopes are a mechanism that allows for treating the output of a number of terms as a single condition. For example, the following query has two terms with an Or operator that are negated by a Not operator:
A query scope can contain any number of terms and operators. The following query has a scope with mixed operators:
Query scopes allow for the creation of complex queries when combined with variables and relationships. The following query finds all entities that have no children with Position:
Note how this is different from this query, which finds all children that don't have Position:
Whereas the first query only returns parents without children with Position, the second query returns parents that have at least one child that doesn't have Position.
When a scope is evaluated, the entire result set of the scope is treated as a single term. This has as side effect that any variables first declared inside the scope are not available outside of the scope. For example, in the following query the value for variable $child is undefined, as it is first used inside a scope:
Scopes currently have the following limitations:
!{ ... }). Future versions of flecs will add support for combining scopes with Or operators (e.g. { ... } || { ... }).The following examples show how to use scopes in the different language bindings:
C
C++
Rust
Flecs Query Language
Source is a property of a term that specifies the entity on which the term should be matched. Queries support two kinds of sources: static and variable. A static source is known when the query is created (for example: match SimTime on entity Game), whereas a variable source is resolved while the query is evaluated. When no explicit source is specified, a default variable source called $this is used (see Variables).
When a query only has terms with fixed sources, iterating the query will return a result at least once when it matches, and at most once if the query terms do not match wildcards. If a query has one or more terms with a fixed source that do not match the entity, the query will return no results. A source does not need to match the query when the query is created.
When a term has a fixed source and the access modifiers are not explicitly set, the access modifier defaults to In, instead of InOut. The rationale behind this is that it encourages code to only makes local changes (changes to components owned by the matched entity) which is easier to maintain and multithread. This default can be overridden by explicitly setting access modifiers.
The following sections show how to use variable and fixed sources with the different language bindings.
C
To specify a fixed source, set the src.id member to the entity to match. The following example shows how to set a source, and how to access the value provided by a term with a fixed source:
A source may also be specified by name by setting the src.name member:
This examples shows how to access the entities matched by the default $this source and a fixed source:
The entities and count member are solely populated by the number of entities matched by the default $this source. If a query only contains fixed sources, count will be set to 0. This is important to keep in mind, as the inner for loop from the last example would never be iterated for a query that only has fixed sources.
C++
To specify a fixed source, call the src method to the entity to match. The following example shows how to set a source, and how to access the value provided by a term with a fixed source:
Note that since SimTime is matched on a single entity, it is accessed as a pointer, not an array. The next example shows how queries with mixed $this and fixed sources can be iterated with each:
Note how each abstracts away the difference between components matched on the (default) $this source and components matched on a single entity.
When a query has no terms for the (default) $this source, it must be iterated with the run function or with a variant of each that does not have a signature with flecs::entity as first argument:
A source may also be specified by name:
Rust
To specify a fixed source, call the set_src_id method to the entity to match. The following example shows how to set a source, and how to access the value provided by a term with a fixed source:
The next example shows how queries with mixed $this and fixed sources can be iterated with each:
Note how each abstracts away the difference between components matched on the (default) $this source and components matched on a single entity.
When a query has no terms for the (default) $this source, it must be iterated with the run function or with a variant of each that does not have a signature with flecs::entity as first argument:
A source may also be specified by name:
Flecs Query Language
To specify a source in the DSL, use parenthesis after the component identifier. The following example uses the default $this source for Position and Velocity, and Game as source for SimTime.
In the previous example the source for Position and Velocity is implicit. The following example shows the same query with explicit sources for all terms:
To specify a source for a pair, the second element of the pair is placed inside the parenthesis after the source. The following query uses the default $this source for the (Color, Diffuse) pair, and Game as source for the (Color, Sky) pair.
In the previous example the source for (Color, Diffuse) is implicit. The following example shows the same query with explicit sources for all terms:
Relationship traversal enables a query to search for a component by traversing a relationship. One of the most common examples of where this is useful is a Transform system, which matches Position on an entity and the entity's parent. To find the Position component on a parent entity, a query traverses the ChildOf relationship upwards:
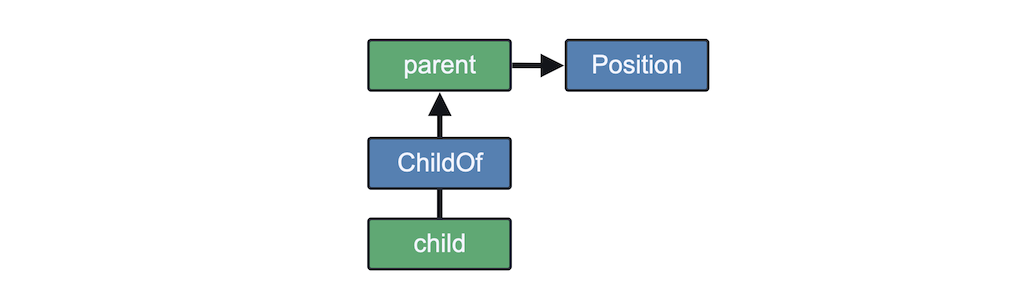
The arrows in this diagram indicate the direction in which the query is traversing the ChildOf relationship to find the component. A query will continue traversing until it has found an entity with the component, or until a root (an entity without the relationship) has been found. The traversal is depth-first. If an entity has multiple instances of a relationship a query will first traverse the first instance until its root entity before continuing with the second instance.
Using the relationship traversal feature will in most cases provide better performance than doing the traversal in user code. This is especially true for cached queries, where the results of traversal are cached. Relationship traversal can in some edge cases cause performance degradation, especially in applications with large numbers of cached queries and deep hierarchies. See the section on performance & rematching for more details.
Any relationship used for traversal must have the Traversable property. Attempting to create a query that traverses a relationship that does not have the Traversable property will cause query creation to fail. This safeguards against creating queries that could end up in an infinite traversal loop when a cyclic relationship is encountered.
Relationship traversal works for both variable and fixed sources.
Traversal behavior can be customized with the following bit flags, in addition to the relationship being traversed:
| Name | DSL identifier | C identifier | C++ identifier | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self | self | EcsSelf | flecs::Self | Match self |
| Up | up | EcsUp | flecs::Up | Match by traversing upwards |
| Cascade | cascade | EcsCascade | flecs::Cascade | Same as Up, but iterate in breadth-first order |
| Desc | desc | EcsDesc | flecs::Desc | Combine with Cascade to iterate hierarchy bottom to top |
If just Self is set a query will only match components on the matched entity (no traversal). If just Up is set, a query will only match components that can be reached by following the relationship and ignore components from the matched entity. If both Self and Up are set, the query will first look on the matched entity, and if it does not have the component the query will continue searching by traverse the relationship.
When an Up traversal flag is set, but no traversal relationship is provided, the traversal relationship defaults to ChildOf. An example:
C
C++
Rust
Query terms default to Self, except for components that have the (OnInstantiate, Inherit) trait. In that case, terms default to Self|Up with the IsA relationship, which matches components inherited from IsA targets (typically prefabs). An example:
C
C++
Rust
When a relationship that is not IsA is traversed, the entities visited while traversing will still be tested for inherited components. This means that an entity with a parent that inherits the Mass component from a prefab will match a query that traverses the ChildOf relationship to match the Mass component. An example:
C
C++
Rust
When a component is matched through traversal and its access modifier is not explicitly set, it defaults to flecs::In. This behavior is consistent with terms that have a fixed source.
This list is an overview of current relationship traversal limitations:
Cascade and Desc flags require caching.The following sections show how to use traversal in the different language bindings.
C
The following example shows a query that matches an inherited component:
The following example shows a query that matches a component from a parent:
The following example shows a query that traverses a custom relationship:
C++
The following example shows a query that matches an inherited component:
The following example shows a query that matches a component from a parent:
The following example shows a query that traverses a custom relationship:
Rust
The following example shows a query that matches an inherited component:
The following example shows a query that matches a component from a parent:
The following example shows a query that traverses a custom relationship:
Flecs Query Language
The following example shows a query that matches a component with the (OnInstantiate, Inherit) trait:
The following example shows a query that matches a component from a parent:
The following example shows a query that traverses a custom relationship:
Query variables represent the state of a query while it is being evaluated. The most common form of state is "the entity (or table) against which the query is evaluated". While a query is evaluating an entity or table, it has to store it somewhere. In flecs, that "somewhere" is a query variable.
Consider this query example, written down with explicit term sources:
The first term to encounter a variable is usually the one to populate it with all candidates that could match that term. Subsequent terms then use the already populated variable to test if it matches. If the condition matches, the query moves on to the next term. If the condition fails, the query moves back to the previous term and, if necessary, populates the variable with the next candidate. These kinds of conditions are usually referred to as predicates, and this evaluation process is called backtracking.
This process effectively constrains the possible results that a term could yield. By itself, the Velocity term would return all entities with the Velocity component, but because $this has been assigned already with entities that have Position, the term only feeds forward entities that have both Position and Velocity.
While using variables as source is the most common application for variables, variables can be used in any part of the term. Consider constructing a query for all spaceships that are docked to a planet. A first attempt could look like this:
When rewritten with explicit sources, the query looks like this:
This returns all spaceships that are docked to anything, instead of docked to planets. To constrain the result of this query, the wildcard used as target for the DockedTo relationship can be replaced with a variable. An example:
When the second term is evaluated for the first time, $Location will not yet be populated. This causes the term to do two things:
$this has (DockedTo, *)$Location with the id matched by *.After evaluating the second term, the $Location variable is populated with the location the spaceship is docked to. We can now use this variable in a new term, that constrains the location to only entities that have Planet:
This query returns the desired result ("return all spaceships docked to a planet").
Variables can also be used to constrain matched components. Consider the following example query:
This query returns serializable components for all entities that have at least one.
Variables can be used as the starting point of a by-name lookup. This can be useful when matching hierarchies that have a well-defined structure. An example:
This query will look for an child entity named cockpit in the scope of the matched entity for $this, and use that entity to match with Powered. If no entity with the name cockpit is found, the term will evaluate to false.
By default variables are assigned while the query is being iterated, but variables can be set before query iteration to constrain the results of a query. Consider the previous example:
An application can set the $this variable or $Location variables, or both, before starting iteration to constrain the results returned by the query. This makes it possible to reuse a single query for multiple purposes, which provides better performance when compared to creating multiple queries.
The following sections show how to use query variables in the different language bindings.
C
Query variables can be specified by setting the name member in combination with setting the EcsIsVariable bit in the flags member:
Alternatively an application can specify a name with the $ prefix to indicate it is a variable:
An application can constrain the results of the query by setting the variable before starting iteration:
C++
Query variables can be specified by specifying a name with a $ prefix:
Alternatively, variables can also be specified using the var method:
An application can constrain the results of the query by setting the variable before starting iteration:
Alternatively the variable name can be provided to set_var directly:
Rust
Query variables can be specified by specifying a name with a $ prefix:
Alternatively, variables can also be specified using the var method:
An application can constrain the results of the query by setting the variable before starting iteration:
Alternatively the variable name can be provided to set_var directly:
Queries can match against the values of component members if they are of the ecs_entity_t type, and the component type is described with the reflection framework. Member value queries make it possible to query on values that can change rapidly without requiring structural changes in the ECS. The tradeoff is that other than with the regular, DontFragment and CanToggle storage options there are no acceleration structures to speed up query evaluation, which means that a query has to evaluate each instance of the component.
The following sections show how to use queries in the different language bindings.
C
C++
Rust
Flecs Query Language
Member value queries can be used in combination with wildcards:
Member value queries can be used in combination with variables:
Change detection makes it possible for applications to know whether data matching a query has changed. Changes are tracked at the table level, for each component in the table. While this is less granular than per entity tracking, the mechanism has minimal overhead, and can be used to skip entities in bulk.
Change detection works by storing a list of counters on tracked tables, where each counter tracks changes for a component in the table. When a component in the table changes, the corresponding counter is increased. An additional counter is stored for changes that add or remove entities to the table. Queries with change detection store a copy of the list of counters for each table in the cache, and compare counters to detect changes. To reduce overhead, counters are only tracked for tables matched with queries that use change detection.
The change detection feature cannot detect all changes. The following scenarios are detected by change detection:
setmodified for an entity/componentinout or out termsThe following scenarios are not detected by change detection:
ensure without calling modifiedecs_ref_t or flecs::ref) without calling modifiedA query with change detection enabled will only report a change for the components it matched with, or when an entity got added/removed to a matched table. A change to a component in a matched table that is not matched by the query will not be reported by the query.
Change detection needs to be explicitly enabled on queries. See the examples below for how to do this in the different language bindings.
When a change occurred in a table matching a query, the query state for that table will remain changed until the table is iterated by the query.
When a query iterates a table for which changes are tracked and the query has inout or out terms that are matched with components of that table, the counter for those components will be increased by default. An application can indicate that no components were modified by skipping the table (see code examples).
When a query uses change detection and has
outorinoutterms, its state will always be changed as iterating the query increases the table counters. It is recommended to only use terms with theinaccess modifier in combination with change detection.
The following sections show how to use change detection in the different language bindings. The code examples use cached queries, which is the only kind of query for which change detection is supported.
C
The following example shows how the change detection API is used in C:
C++
The following example shows how the change detection API is used in C++:
Rust
The following example shows how the change detection API is used in C++:
Sorted queries allow an application to specify a component that entities should be sorted on. Sorting is enabled by setting the order_by function in combination with the component to order on. Sorted queries sort the tables they match with when necessary. To determine whether a table needs to be sorted, sorted queries use change detection. A query determines whether a sort operation is needed when an iterator is created for it.
Because sorting relies on change detection, it has the same limitations with respect to detecting changes. When using sorted queries, make sure a query is able to detect the changes necessary for knowing when to (re)sort.
Query sorting works best for data that does not change often, as the sorting process can be expensive. This is especially true for queries that match with many tables, as one step of the sorting algorithm scans all matched tables repeatedly to find an ordered set of slices.
An application should also prevent having sorted queries with conflicting sorting requirements. This can cause scenarios in which both queries are invalidating each others ordering, which can result in a resort each time an iterator is created for one of the conflicting queries.
Sorted queries are encouraged to mark the component used for sorting as In. If a sorted query has write access to the sorted component, iterating the query will invalidate its own order which can lead to continuous resorting.
Components matched through traversal can be used to sort entities. This often results in more efficient sorting as component values can be used to sort entire tables, and as a result tables themselves do not have to be sorted.
Sorted queries use a two-step process to return entities in a sorted order. The sort algorithm used in both steps is quicksort. The first step sorts contents of all tables matched by the query. The second step is to find a list of ordered slices across the tables matched by the query. This second step is necessary to support datasets where ordered results have entities interleaved from multiple tables. An example data set:
| Entity | Components (table) | Value used for sorting |
|---|---|---|
| E1 | Position | 1 |
| E2 | Position | 3 |
| E3 | Position | 4 |
| E4 | Position, Velocity | 5 |
| E5 | Position, Velocity | 7 |
| E6 | Position, Mass | 8 |
| E7 | Position | 10 |
| E8 | Position | 11 |
To make sure a query iterates the entities in the right order, it will iterate entities in the ordered tables to determine the largest slice of ordered entities in each table, which the query will iterate in order. Slices are computed during the sorting step. For the above set of entities slices would look like this:
| Table | Slice |
|---|---|
| Position | 0..2 |
| Position, Velocity | 3..4 |
| Position, Mass | 5 |
| Position | 6..7 |
To minimize time spent on sorting, the results of a sort are cached. The performance overhead of iterating an already sorted query is comparable to iterating a regular query, though for degenerate scenarios where a sort produces many slices for comparatively few tables the performance overhead can be significant.
The following sections show how to use sorting in the different language bindings. The code examples use cached queries, which is the only kind of query for which change detection is supported.
C
The following example shows how to use sorted queries in C:
The function signature of the order_by function should look like the following example:
A query may only use entity identifiers to sort by not setting the order_by member:
The following example shows a function that sorts by entity id:
C++
The following example shows how to use sorted queries in C++:
Queries may specify a component id if the component is not known at compile time:
Queries may specify zero for component id to sort on entity ids:
Rust
The following example shows how to use sorted queries in Rust:
Queries may specify a component id if the component is not known at compile time:
Queries may specify zero for component id to sort on entity ids:
Grouping is the ability of queries to assign an id ("group id") to a set of tables. Grouped tables are iterated together, as they are stored together in the query cache. Additionally, groups in the query cache are sorted by group id, which guarantees that tables with a lower group id are iterated after tables with a higher group id. Grouping is only supported for cached queries.
Group ids are local to a query, and as a result queries with grouping do not modify the tables they match with.
Grouping is the least granular, most efficient mechanism to order results of a query. Grouping does not rely on sorting individual tables or entities. Instead, sorting only happens when a new group id is introduced to a query, which is rare in many scenarios. Queries maintain an index that maps group ids to the first and last elements in the cache belonging to that group. This allows for tables to be inserted into the cache in a fast constant time operation, while also providing ordered access to tables.
The grouping mechanism is used internally by the cascade feature. Queries that use cascade use a computed hierarchy depth as group id. Because lower group ids are iterated before higher group ids, this provides in a bread-first topological sort of tables and entities that is almost free to maintain.
Queries may be grouped and sorted at the same time. When combined, grouping takes precedence over sorting. Tables are first assigned to their groups in the query cache, after which each group is sorted individually.
An example of an internal query that uses cascade grouping in combination with sorting is the builtin pipeline query. The pipeline query first groups systems by their depth in the DependsOn relationship tree. Within the depth-based groups systems are ordered based on their entity id, which ensures systems are iterated in order of declaration.
A group iterator iterates over a single group of a grouped query. This can be useful when an application may need to match different entities based on the context of the game, such as editor mode, day/night, inside/outside or location in the world.
One example is that of an open game which is divided up into world cells. Even though a world may contain many entities, only the entities in cells close to the player need to be processed. Instead of creating a cached query per world cell, apps can create a single query grouped by world cell, and use group iterators to only iterate the necessary cells.
Grouped iterators, when used in combination with a good group_by function are one of the fastest available mechanisms for finding entities in Flecs. The feature provides the iteration performance of having a cached query per group, but without the overhead of having to maintain multiple caches. Whether a group has ten or ten thousand tables does not matter, which makes the feature an enabler for games with large numbers of entities.
The following sections show how to use grouping in the different language bindings. The code examples use cached queries, which is the only kind of query for which change detection is supported.
C
The following example shows how grouping can be used to group entities that are in the same game region.
The following example shows what the implementation of group_by_target could look like:
When no value for group_by_callback is provided, it will default to an internal function with the same behavior as group_by_target. An example:
To iterate entities in a single group, use the ecs_iter_set_group function:
C++
The following example shows how grouping can be used to group entities that are in the same game region.
When no group_by functions, it will default to an internal function with the same behavior as the previous example. An example:
To iterate entities in a single group, use the set_group function:
Rust
This section for Rust is unfinished. For code examples, see the group_by examples in the examples/flecs/queries folder. Note, this still partially uses the C API. Until the Rust API is updated, this section will remain unfinished.
The following example shows how grouping can be used to group entities that are in the same game region.
When no group_by functions, it will default to an internal function with the same behavior as the previous example. An example:
To iterate entities in a single group, use the set_group function:
Component inheritance allows for a query to match entities with a component and all subsets of that component, as defined by the IsA relationship. Component inheritance is enabled for all queries by default, for components where it applies.
It is possible to prevent inheriting from a component from by adding the Final property. Queries for components with the Final property will not attempt to resolve component inheritance.
Inheritance relationships can, but are not required to mirror inheritance of the types used as long as it does not impact the layout of the type. Component inheritance is most often used with tags.
The following sections show how to use component inheritance in the different language bindings.
C
The following example shows a query that uses component inheritance to match entities:
C++
The following example shows a query that uses component inheritance to match entities:
Rust
The following example shows a query that uses component inheritance to match entities:
When a transitive relationship is used by a query, a query will automatically look up or test against pairs that satisfy the transitive property. Transitivity is usually defined as:
If R(X, Y) and R(Y, Z) then R(X, Z)
In this example, R is the transitive relationship and X, Y and Z are entities that are used both as source and second element. A typical example of a transitive relationship is LocatedIn. If Bob (X) is located in Manhattan (Y) and Manhattan (Y) is located in New York (Z), then Bob (X) is also located in New York (Z). Therefore "located in" is transitive.
A relationship can be made transitive by adding the transitive property. This would ensure that both (LocatedIn, ManHattan) and (LocatedIn, NewYork) queries would match Bob. When the location is replaced with a variable, the variable will assume all values encountered while traversing the transitive relationship. For example, (LocatedIn, $Place) would return results with Place = [ManHattan, NewYork] for Bob, and a result with Place = [NewYork] for ManHattan.
An example of a builtin relationship that has the Transitive property is the IsA relationship.
Transitive traversal can be disabled for a term with a transitive relationship by adding the Self flag to the second element of the pair.
The following sections show how to use transitive relationships in the different language bindings.
C
The following example shows a query that uses transitivity to match entities that are located in New York:
Queries for transitive relationships can be compared with variables. This query returns all locations an entity is in:
Variables can be used to constrain the results of a transitive query. The following query returns locations an entity is in that are a city:
C++
The following example shows a query that uses transitivity to match entities that are located in New York:
Queries for transitive relationships can be compared with variables. This query returns all locations an entity is in:
Variables can be used to constrain the results of a transitive query. The following query returns locations an entity is in that are a city:
Rust
The following example shows a query that uses transitivity to match entities that are located in New York:
Queries for transitive relationships can be compared with variables. This query returns all locations an entity is in:
Variables can be used to constrain the results of a transitive query. The following query returns locations an entity is in that are a city:
Flecs Query Language
Transitivity in a query is enabled by adding the Transitive property to a relationship. As a result, a query for a transitive relationship looks the same as a query for a non-transitive relationship. The following examples show the queries used in the C/C++ examples:
Match all entities located in New York:
Return all locations an entity is in:
Return the city entities are in:
When a query matches a reflexive relationship, a query term will evaluate to true if the source and target are equal. Reflexivity can be defined as:
R(X, X)
For example, if relationship IsA (R) is reflexive, then a Tree (X) is a Tree (X). An example of a builtin relationship that has the Reflexive property is the IsA relationship.
The following sections show how to use transitive relationships in the different language bindings.
C
The following example shows a query that uses the IsA reflexive relationship:
C++
The following example shows a query that uses the IsA reflexive relationship:
Rust
The following example shows a query that uses the IsA reflexive relationship:
Flecs Query Language
Reflexivity in a query is enabled by adding the Reflexive property to a relationship. As a result, a query for a reflexive relationship looks the same as a query for a non-reflexive relationship. The following example shows the query used in the C/C++ examples: